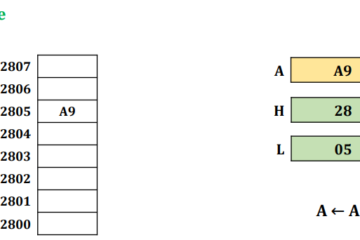
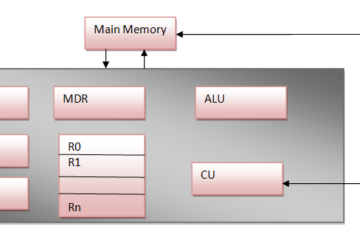
I/O channels and I/O Processors
I/O Channels: Definition: An I/O channel, also known as an I/O channel controller or I/O channel processor, is a specialized processor or controller dedicated to managing data transfers between the CPU and peripheral devices. Functionality: I/O channels handle the details of data transfer, including managing communication protocols, buffering, error detection Read more…